#Day6 #90DaysofDevOps
The concept of Linux File permission and ownership is important in Linux. Today, we will be working on Linux permissions and ownership and will do tasks on both of them. Let us start with the Permissions.
Create a simple file and do ls -ltr to see the details of the files
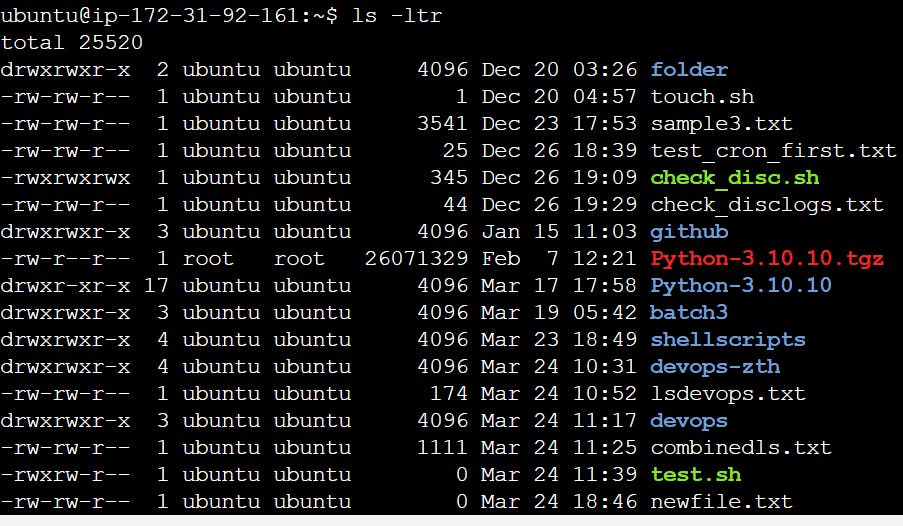
Each of the three permissions are assigned to three defined categories of users. The categories are:
owner - The owner of the file or application
"chown" - used to change the ownership permission of a file or directory.
group - The group that owns the file or application.
"chgrp" is used to change the group permission of a file or directory.
others - All users with access to the system. (outside users are in a group)
"chmod" is used to change the other users permissions of a file or directory.
As a task, change the user permissions of the file and note the changes after
ls -ltr
What are File permissions -
Linux is a multi-user operating system, so it has security to prevent people from accessing each other's confidential files.
When you execute an “ls” command, you are not given any information about the security of the files, because by default “ls” only lists the names of files. You can get more information by using an “option” with the “ls” command. All options start with a ‘-‘. For example, to execute “ls” with the “long listing” option, you would type ls -l
The first character will almost always be either a ‘-‘, which means it’s a file, or a ‘d’, which means it’s a directory.
The next nine characters (rw-r–rwx) show the security and permissions from which -
r = reading permissions
w = writing permissions
x = executable permissions
What is ACL?
Access control list provides an additional, more flexible permission mechanism for file systems. It is designed to assist with UNIX file permissions. ACL allows us to give permissions for any user or group to any disc resource.
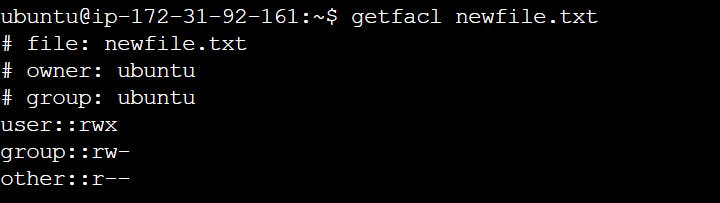
getfacl command
The getfacl command is used to retrieve the ACLs of files and directories.
setfact command
The setfacl command in Linux is used to set file access control lists. A file’s ACL specifies the users and groups that are allowed to access the file, and the permissions that they have. The setfacl command can be used to add, remove, or modify a file’s ACL.