Kubernetes Overview
With the widespread adoption of containers among organizations, Kubernetes, the container-centric management software, has become a standard to deploy and operate containerized applications and is one of the most important parts of DevOps.
Originally developed at Google and released as open-source in 2014. Kubernetes builds on 15 years of running Google's containerized workloads and the valuable contributions from the open-source community.
Tasks
What is Kubernetes? Write in your own words and why do we call it k8s?
Kubernetes is a portable, extensible, open source platform for managing containerized workloads and services, that facilitates both declarative configuration and automation. It has large, rapidly growing ecosystem.
Containers are a good way to bundle and run applications Containers are a good way to bundle and run your applications. In a production environment, you need to manage the containers that run the applications and ensure that there is no downtime. For example, if a container goes down, another container needs to start. Wouldn't it be easier if this behavior was handled by a system?
That's how Kubernetes comes to the rescue! Kubernetes provides you with a framework to run distributed systems resiliently. It takes care of scaling and failover for your application, provides deployment patterns, and more. For example: Kubernetes can easily manage a canary deployment for your system.
The name K8s is an abbreviation results from counting the letters between K and s which are 8 in number. Hence 'K8s'.
What are the benefits of using k8s?
Kubernetes provides with the following -
Service discovery and load balancing
Storage orchestration
Automated rollouts and rollbacks
Automatic bin packing
Self-healing
Secret and configuration management.
Explain the architecture of Kubernetes.
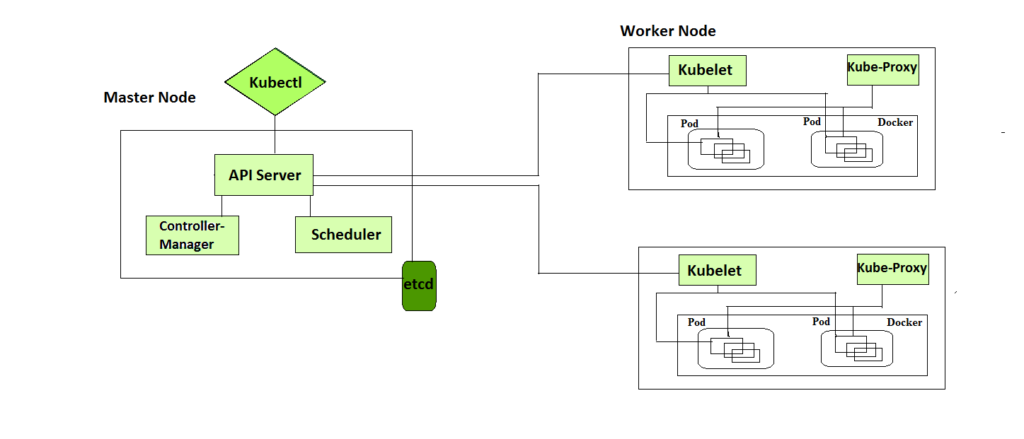
Api server - The API server is a component of the Kubernetes control plane that exposes the Kubernetes API. It is like an initial gateway to the cluster that listens to updates or queries via CLI like Kubectl. Kubectl communicates with API Server to inform what needs to be done like creating pods or deleting pods etc. It also works as a gatekeeper. It generally validates requests received and then forwards them to other processes. No request can be directly passed to the cluster, it has to be passed through the API Server.
Kube Scheduler - When API Server receives a request for Scheduling Pods then the request is passed on to the Scheduler. It intelligently decides on which node to schedule the pod for better efficiency of the cluster.
Kube-Control-Manager - It is responsible for running the controllers that handle the various aspects of the cluster’s control loop. These controllers include the replication controller, which ensures that the desired number of replicas of a given application is running, and the node controller, which ensures that nodes are correctly marked as “ready” or “not ready” based on their current state.
etcd - It is a key-value store of a Cluster. The Cluster State Changes get stored in the etcd. It acts as the Cluster brain because it tells the Scheduler and other processes about which resources are available and about cluster state changes.
Node components -
Container runtime - A container runtime is needed to run the application containers running on pods inside a pod. Example-> Docker
kubelet - It interacts with both the container runtime as well as the Node. It is the process responsible for starting a pod with a container inside.
kube-proxy - It is the process responsible for forwarding the request from Services to the pods. It has intelligent logic to forward the request to the right pod in the worker node.

What is Control Plane?
It is a collection of various components that help us in managing the overall health of a cluster. For example, if you want to set up new pods, destroy pods, scale pods, etc. 4 services run on Control Plane:
Kube-API server
Kube-Scheduler
Kube-Contoller-Manager
etcd
Write the difference between kubectl and kubelets.
kubectl is the command line interface (CLI) tool for working with a Kubernetes cluster. kubelet is the technology that applies, creates, updates and destroys containers on a Kubernetes node.
kubectl is the primary means by which a developer can interact with a Kubernetes cluster.
Kubelet on the other hand is a process that runs on each node of a Kubernetes cluster and creates, destroys, or update pods and their Docker containers for the given node when instructed to do so.
Explain the role of the API server.
The API server is a component of the Kubernetes control plane that exposes the Kubernetes API. It is like an initial gateway to the cluster that listens to updates or queries via CLI like Kubectl. Kubectl communicates with API Server to inform what needs to be done like creating pods or deleting pods etc. It also works as a gatekeeper. It generally validates requests received and then forwards them to other processes. No request can be directly passed to the cluster, it has to be passed through the API Server.
